
In geology, the study of mineral precipitation can provide insights into the history and composition of rocks. They are also used in wastewater treatment, where they help remove harmful substances from the water. For example, precipitation reactions are used to identify unknown substances in chemical analysis. Applications of Precipitation in Science Precipitation has many practical applications in different fields of science. Temperature and pressure also play significant roles in precipitation, especially in the formation of minerals and crystals. Some compounds may only precipitate at certain pH values. Another factor that affects the formation of precipitates is pH. The higher the concentration of the reactants, the more likely a reaction will occur. One of the most critical factors is the concentration of the reactants in the solution. Factors Affecting Precipitation Several factors can affect the formation of precipitates.

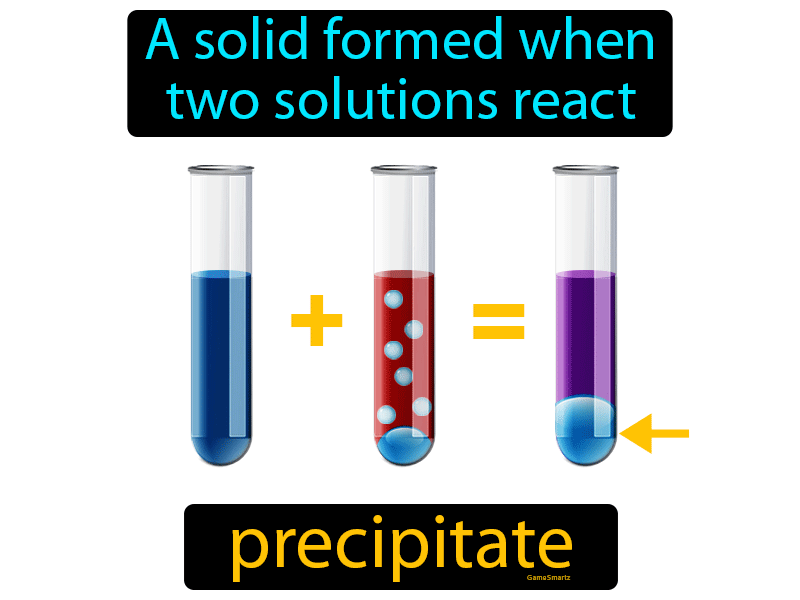
For example, snowflakes are formed by the crystallization of water molecules when the temperature drops below freezing point. Other types of precipitates are formed by changes in temperature or pressure. Examples of these types of precipitates include silver chloride, lead iodide, and calcium carbonate. In some cases, precipitates are formed by the addition of a precipitating agent or reactant to the solution. Types of Precipitates There are several types of precipitates, depending on how they are formed. Precipitation is a vital process in chemistry, with numerous applications in various fields of science. This process is also known as a precipitation reaction, and the insoluble solid that is formed is called the precipitate. "Precipitation Definition In Chemistry" ~ bbaz What is Precipitation in Chemistry? Precipitation is a chemical reaction that occurs when two soluble compounds in a solution react to form an insoluble compound, which then separates from the solution as a solid. So grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the fascinating world of precipitation in chemistry. You will learn about the different types of precipitates, how they form, and the factors that affect their formation.

From understanding the formation of snowflakes to studying the formation of minerals in rocks, there’s so much to discover! Whether you’re a chemistry student, a researcher, or simply someone who wants to know more about the world around you, reading this article will provide you with a comprehensive definition of precipitation. In this article, we will explore the concept of precipitation and its various applications in science. Have you ever wondered how rain forms in the clouds or why certain medications have to be kept at a specific temperature? The answer lies in precipitation chemistry. Understanding precipitation is crucial in many fields of science, including medicine, geology, and environmental science. This compound, also known as a precipitate, falls out of solution and settles at the bottom of the container. It’s a process that occurs when two or more substances interact to form an insoluble compound. (You cannot swap both you would end up with the same substances you started with.) Either perspective should allow you to predict the proper products, as long as you pair a cation with an anion and not a cation with a cation or an anion with an anion.Precipitation is one of the most fascinating phenomena in chemistry. There are two equivalent ways of considering a double-replacement equation: either the cations are swapped, or the anions are swapped.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
